Workflow¶
In this section we will describe in details the available workflow processes, since the setup until the end summary. The following examples are going to assume the usage of a sequential bot with TCP communication and JSON information format.
Basic Workflow¶
The overview of what happens when pitaya-bot is started:
- Initialization of app, configuration fetch, specs directory lookup and creation of metric reporters
- Instantiation of many go routines, which are defined in spec files
- Validation of selected bot and written specs
- Execution of specs
- Notification of the result to all of metrics reporter
- Summarization of tests
Initialization¶
The first thing pitaya-bot does is instantiate an App struct based on the config file, receiving the metric reporters that will be used (Promethues, …) and name of the pitaya game which will be tested.
The configuration is also passed to the bots that will follow the specs, so that they know which storage will be used, endpoint to access, etc.
Another important point is the directory where the specs are located, because it will use the number of spec files as the number of go routines that will execute each one of them in a parallel way.
Instances¶
Based on the spec file, the field numberOfInstances will dictate how many go routines will be created to run each of the written scenarios.
Validation¶
For each spec, it will validate if it was able to:
- Create the given type of bot
- Initialize the bot
- Run the given spec without problems
- Finalize the bot
Execution of given spec¶
In the moment that the bot is initialized, it will fetch all the information contained in the spec and create operations that will be executed. The operations can vary, it can make all the possible operations that a pitaya client can do and also store informations from the received responses. It is important to mention that each bot has different operations that can be used, so consult them before writing your own testing scenarios.
Metric Reporter¶
After each request to a pitaya server, the pitaya-bot will inform the metric reporter of the response time, which is important to see the overall QoS(Quality of Service).
Summary¶
After all specs have been run, it will gather all the results obtained and return in the terminal, informing if it was a total success or if some errors occurred.
Workflows¶
There is the listing of all possible workflows:
- Local: Pitaya-bot will be instantiated locally and will request the server from current location
- Local Manager: A Pitaya-Bot manager will be instantiated locally and will create the Kubernetes Jobs inside kubernetes cluster from given config and specs
- Remote Manager: A Pitaya-Bot manager will be instantiated inside a kubernetes cluster and will create the Kubernetes Jobs from given config and specs
Local¶
It will instantiate an unit of pitaya-bot, which will run all specs located inside given directory. Each spec file will be run in a distinct go routine and also, each operation from the spec will be run in another distinct go routine.
The local architecture is represented below:

Local Manager¶
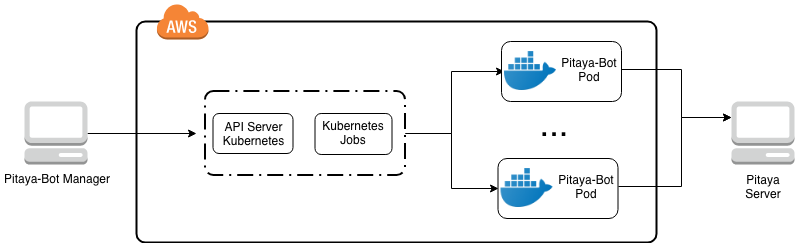
It will instantiate a pitaya-bot manager, which will create all configmaps, containing all specs and the config.yaml, to be used by each kubernetes job. After creating all configmaps and jobs, it will start a controller, that will be watching all the jobs created and after all of them finish their work or time out, it will clean everything that was created inside the kubernetes cluster.
The local manager architecture is represented below:
Remote Manager¶
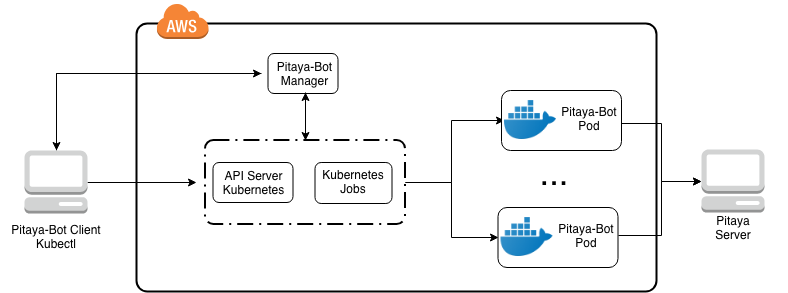
It will instantiate a pitaya-bot manager inside kubernetes cluster, which will create all configmaps, containing all specs and config.yaml, to be used by each kubernetes job. After creating all configmaps and jobs, it will start a controller, that will be watching all the jobs created and after all of them finish their work or time out, it will clean everything that was created and will also delete itself with the its configmaps.
The remote manager architecture is represented below:
Deploy Manager¶
It will create a kubernetes deployment, which will be running a pitaya-bot remote manager inside a kubernetes cluster.
Delete All¶
It will delete everything that is related to pitaya-bot inside the kubernetes cluster and is mentioned in the config.yaml.